A trademark search helps you check if your desired business name, logo, or slogan is already taken before you invest time and money in branding. This guide is for entrepreneurs, small business owners, and anyone planning to launch a product or service who needs to verify their trademark is available.
You’ll learn how to use free government databases like the USPTO trademark search system, plus explore international options for Canada trademark search and UK trademark search needs. We’ll also cover how to prepare an effective search strategy and analyze your results to make informed decisions about moving forward with your trademark application.
Preparing Your Search Strategy
Define your trademark concept and variations
Start by clearly describing your trademark in simple terms. Write down exactly what you want to protect – whether it’s a business name, product name, slogan, or logo design. Don’t just stick to the exact spelling or format you plan to use. Think about how customers might search for your brand or how competitors might try to create something similar.
Consider different versions of your trademark that could cause confusion in the marketplace. If your brand name is “QuickFix,” also think about “Quick Fix,” “Kwik Fix,” “Quick-Fix,” and even phonetically similar variations like “Quik Fiks.” Include abbreviations, acronyms, and common misspellings that people might use when searching online.
Pay special attention to how your trademark might appear in different contexts. A logo might work differently than just text, and a stylized version could be distinct from a plain word mark. Document all these variations because each one needs to be checked during your USPTO trademark search.
Create a comprehensive list of similar terms and synonyms
Brainstorm words that mean the same thing as your trademark or convey similar concepts. This step often reveals potential conflicts that aren’t immediately obvious. If your trademark includes the word “swift,” also search for “fast,” “rapid,” “quick,” “speedy,” and “express.”
Think about your industry’s specific language and jargon. Different fields use different terms for the same concepts. In technology, you might need to check both “app” and “application,” while in food service, “bistro,” “café,” “eatery,” and “restaurant” could all be relevant.
Don’t forget foreign language equivalents, especially if you plan to expand internationally or if your target market includes speakers of other languages. A Canada trademark search or UK trademark search might reveal conflicts with translated versions of your trademark.
Create categories for your synonym list: direct synonyms, related concepts, industry terms, slang expressions, and abbreviated forms. This systematic approach helps ensure you don’t miss important variations during your search.
Determine relevant industry classifications
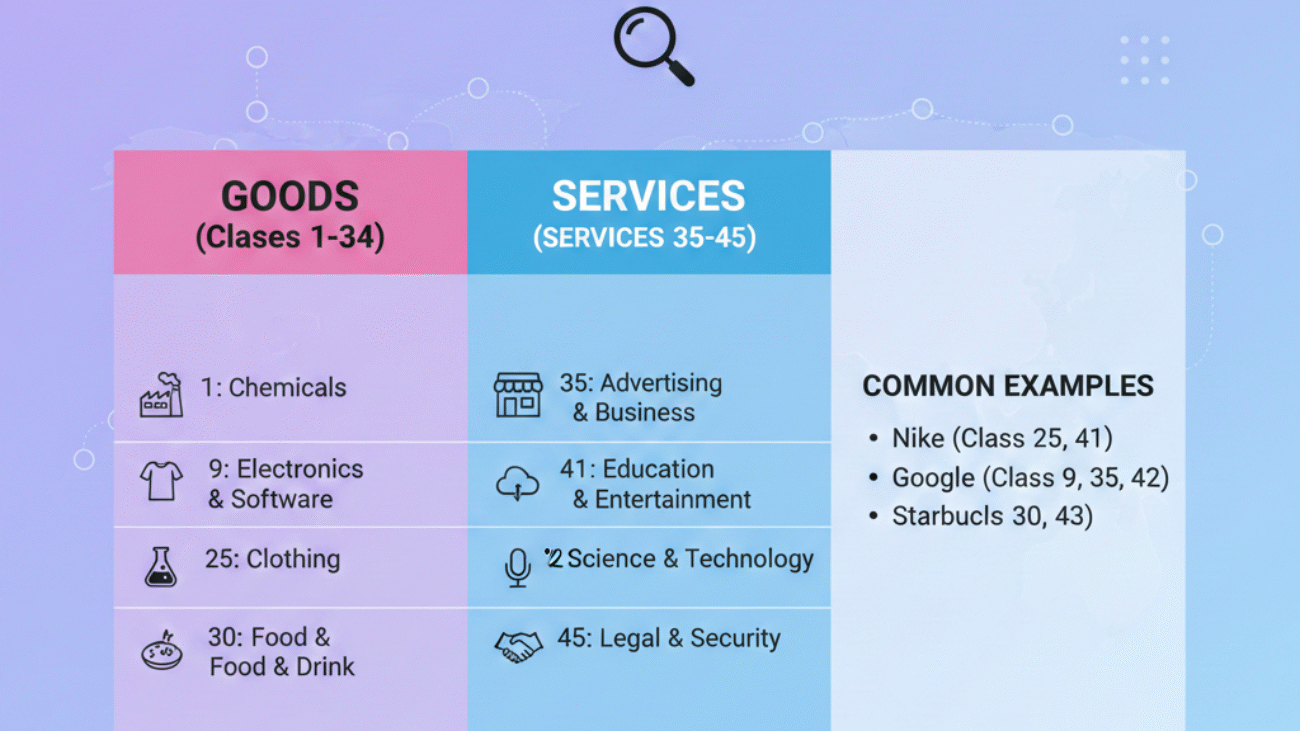
Understanding trademark classifications is crucial for an effective US trademark search. The Nice Classification system divides goods and services into 45 different classes, and trademarks are registered within specific classes. Your search needs to cover the classes where your trademark will be used and where similar businesses operate.
Start with the obvious classifications for your business. If you’re launching a clothing brand, Class 25 covers clothing and footwear. But don’t stop there – consider related classes too. Your clothing brand might also need Class 35 for retail services or Class 42 if you plan to offer design services.
Research where your competitors have registered their trademarks. This gives you insight into which classifications are most relevant in your industry. A software company might register in Class 9 for computer software, Class 42 for software development services, and Class 35 for business services.
Some businesses span multiple classifications. A restaurant might need Class 43 for restaurant services, Class 29 and 30 for packaged foods, Class 32 for beverages, and Class 41 if they offer cooking classes. Missing a relevant classification during your search could mean overlooking a trademark that blocks your registration.
Using Free Government Trademark Databases
Navigate the USPTO trademark database effectively
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) offers the most comprehensive free resource for conducting a USPTO trademark search. The Trademark Electronic Search System (TESS) serves as your primary tool for searching registered trademarks and pending applications in the United States.
Start by accessing TESS through the USPTO website and selecting either the Basic Word Mark Search for simple queries or the Word and/or Design Mark Search for more complex searches. When conducting your US trademark search, begin with broad terms related to your mark, then narrow down using specific search criteria like goods and services classifications, filing dates, or trademark status.
The database allows you to search using various parameters including owner names, serial numbers, registration numbers, and design codes. For word marks, search for phonetic equivalents and alternative spellings that might sound similar to your proposed trademark. Remember that trademark protection extends beyond exact matches – marks that create confusion among consumers can still pose legal challenges.
Use Boolean operators like AND, OR, and NOT to refine your searches effectively. For example, searching “coffee AND shop” will return results containing both terms, while “coffee NOT shop” excludes results with “shop” in them.
Search international trademark databases
Expanding your trademark search beyond US borders requires accessing international databases to ensure comprehensive protection. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Global Brand Database provides free access to over 40 million trademark records from participating countries and regions.
For Canada trademark search activities, the Canadian Intellectual Property Office (CIPO) maintains the Canadian Trademarks Database, which includes active registrations, applications, and abandoned marks. The search interface allows you to filter by trademark type, status, and Nice Classification numbers.
The European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) eSearch plus database covers EU trademark registrations and applications. This resource proves essential if you plan to expand into European markets. For UK trademark search purposes following Brexit, use the UK Intellectual Property Office database, which now operates independently from the EU system.
Other significant databases include Japan’s J-PlatPat system, Australia’s IP Australia database, and China’s Trademark Office database. Each system has unique search capabilities and interfaces, so familiarize yourself with the specific search syntax and available filters for each database.
Understand database search results and status meanings
Database search results contain crucial information that determines your trademark’s viability. Each record displays the trademark’s current status, which directly impacts your ability to register a similar mark. “Live” or “Active” status means the trademark remains protected and enforceable, while “Dead” or “Abandoned” indicates the mark no longer enjoys protection.
Pay close attention to filing dates and registration dates, as these establish priority rights. Earlier filed marks typically receive stronger protection, even if they’re still pending registration. The “first use in commerce” date shows when the owner began using the mark commercially, which can affect trademark strength.
Goods and services classifications, organized under the Nice Classification system, define the scope of trademark protection. A registered mark in Class 25 (clothing) doesn’t automatically prevent registration of a similar mark in Class 9 (electronics), though famous marks receive broader protection across multiple classes.
Examine the mark’s description field for important details about design elements, colors, or stylization that might affect similarity determinations. Some registrations include disclaimers that limit protection to specific elements of the mark.
Save and organize your search findings
Systematic organization of your trademark search results enables effective analysis and future reference. Create a comprehensive spreadsheet documenting each relevant mark you discover, including registration numbers, owners, filing dates, status information, and classification details.
Screenshot or save PDF copies of complete trademark records, as database information can change over time. Organize files using a consistent naming convention that includes the mark name, registration number, and search date.
Document your search methodology by recording the databases searched, keywords used, and date ranges covered. This documentation proves valuable if you need to demonstrate the thoroughness of your search to attorneys or during potential disputes.
Consider using trademark watching services or setting up saved searches in databases that offer this feature. These tools can alert you to new filings that might conflict with your mark, allowing you to monitor the trademark landscape continuously even after your initial search.
Maintain separate folders for different trademark classes and jurisdictions to keep your research organized and easily accessible for decision-making purposes.
Taking Action Based on Your Results
Proceed with trademark application when clear
When your trademark search reveals a clean path ahead, you can move forward with confidence. A clear search result means no identical or confusingly similar marks exist in your business category. This green light allows you to file your application through the USPTO trademark search system or the appropriate government database for your jurisdiction.
Before filing, double-check that your search covered all relevant classifications and geographic areas where you plan to use the trademark. A comprehensive us trademark search should include federal databases, state registrations, and common law usage. Document your search findings carefully – this documentation supports your application and demonstrates due diligence.
File your application promptly after completing your search. Trademark rights often follow a “first to file” principle, meaning delays could allow competitors to claim similar marks. Prepare all required materials, including specimens showing how you’ll use the trademark, detailed descriptions of goods or services, and filing fees.
Modify your trademark to avoid conflicts
Discovering conflicts doesn’t mean abandoning your trademark entirely. Strategic modifications can often resolve potential issues while preserving your brand’s core identity. Small changes to spelling, design elements, or wording might be enough to distinguish your mark from existing ones.
Consider altering visual elements if you’re dealing with logo conflicts. Change fonts, colors, graphic elements, or overall design structure. For word marks, explore synonyms, different spellings, or adding distinctive terms that relate to your business. Adding descriptive words that specify your industry or location can help differentiate your mark.
Test modified versions through additional searches before settling on changes. Each variation requires its own canada trademark search or uk trademark search depending on your target markets. Remember that modifications should maintain your brand’s recognition value while creating sufficient legal distance from conflicting marks.
Evaluate how changes might affect your marketing plans and customer recognition. Sometimes minor adjustments preserve brand strength better than major overhauls. Consider trademark family strategies where you file multiple related marks that work together to protect your brand ecosystem.
Consult with trademark attorneys for complex cases
Complex search results demand professional legal expertise. Situations involving similar marks in related industries, international trademark issues, or ambiguous classification boundaries require specialized knowledge. Trademark attorneys understand nuanced legal concepts like likelihood of confusion, trademark strength, and fair use doctrines.
Attorneys can perform more sophisticated searches using professional databases and legal analysis tools. They access resources beyond basic government databases, including industry-specific databases and international trademark records. Professional searches often reveal potential conflicts that basic searches miss.
Legal counsel becomes essential when dealing with pending applications, abandoned marks that might be revived, or opposition proceedings. Attorneys understand timing requirements, response deadlines, and procedural requirements that could make or break your application. They also negotiate coexistence agreements when appropriate, allowing multiple parties to use similar marks under specific conditions.
Consider attorney consultation costs as insurance against expensive legal disputes later. Early legal investment often prevents costly rebranding, litigation, or trademark abandonment. Many attorneys offer initial consultations to assess your situation and recommend appropriate next steps based on your specific circumstances and business goals.